How does land-based pollution threaten coral reefs?
Many serious coral reef ecosystem stressors originate from land-based sources, most notably toxicants, sediments, and nutrients.
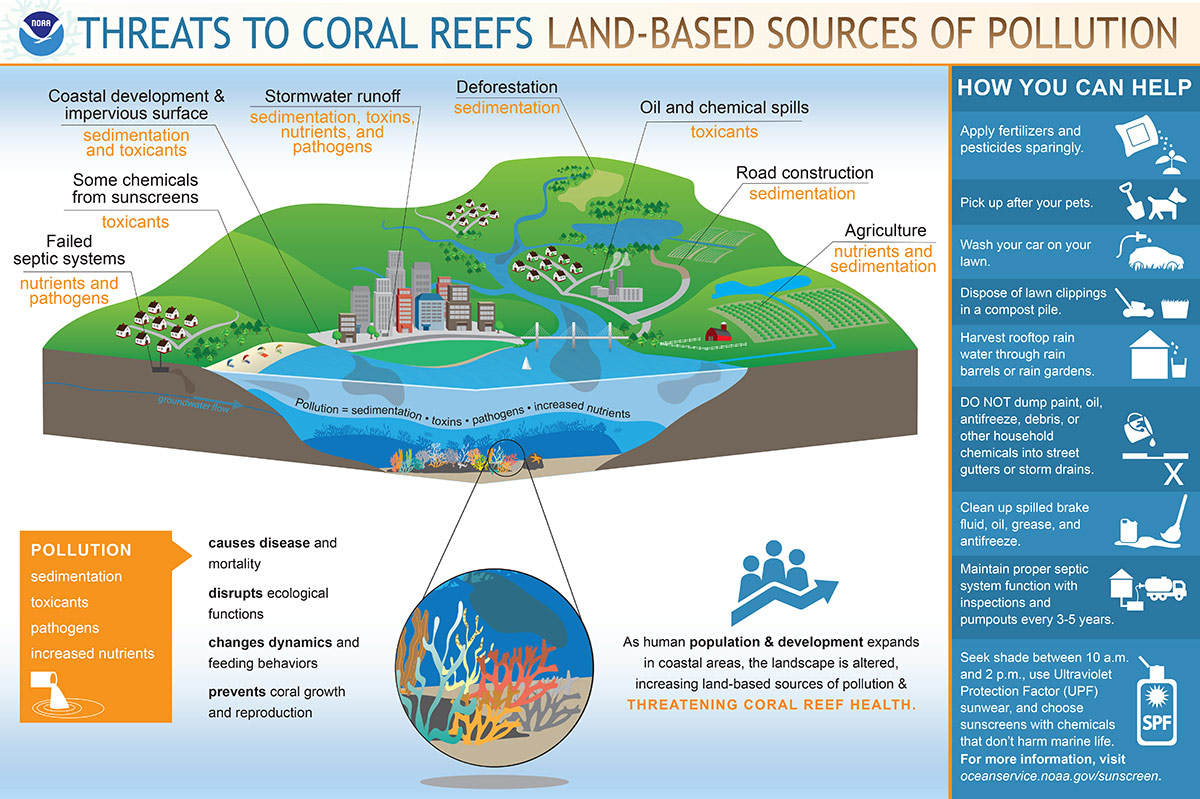
As human population and development expands in coastal areas, the landscape is altered, increasing land-based sources of pollution and threatening coral reef health. Download this infographic | Infographic Text
Impacts from land-based sources of pollution—including coastal development, deforestation, agricultural runoff, and oil and chemical spills—can impede coral growth and reproduction, disrupt overall ecological function, and cause disease and mortality in sensitive species. It is now well accepted that many serious coral reef ecosystem stressors originate from land-based sources, most notably toxicants, sediments, and nutrients.
Within the U.S., there are numerous locations where coral reef ecosystems are highly impacted by watershed alteration, runoff, and coastal development. On U.S. islands in the Pacific and Caribbean, significant changes in the drainage basins due to agriculture, deforestation, grazing of feral animals, fires, road building, and urbanization have increased the volume of land-based pollution released to adjacent coral reef ecosystems.
Many of these issues are made worse because of the geographic and climatic characteristics found in tropical island areas. Together they create unique management challenges.
Infographic Text
Threats to coral reefs: land-based sources of pollution
As human population and development expands in coastal areas, the landscape is altered, increasing land-based source of pollution and threatening coral reef health.
Pollution (e.g., sedimentation, toxins, pathogens, increased nutrients):
- Causes disease and mortality.
- Disrupts ecological functions.
- Changes dynamics and feeding behaviors.
- Prevents coral growth and reproduction.
Land-based sources of pollution include:
- Failed septic systems: nutrients and pathogens.
- Coastal development & impervious surface: sedimentation and toxins.
- Stormwater runoff: sedimentation, toxins, nutrients, and pathogens.
- Deforestation: sedimentation.
- Oil and chemical spills: toxins.
- Road construction: sedimentation.
- Agriculture: nutrients and sedimentation.
How you can help!
- Apply fertilizers and pesticides sparingly.
- Pick up after your pets.
- Wash your car on your lawn.
- Dispose of lawn clippings in a compost pile.
- Harvest rooftop rain water through rain barrels or rain gardens.
- DO NOT dump paint, oil, antifreeze, debris, or other household chemicals into street gutters or storm drains.
- Clean up spilled brake Fluid, oil,greaseand antifreeze
- Maintain proper septic system function with inspections and pumpouts every 3-5 years.
- Seek shade between 10 am & 2 pm, use Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) sunwear, and choose sunscreens with chemicals that don’t harm marine life.
Search Our Facts
Get Social
More Information
Last updated: 06/16/24
Author: NOAA
How to cite this article

