What is bombogenesis?
Bombogenesis is a popular term that describes a midlatitude cyclone that rapidly intensifies.
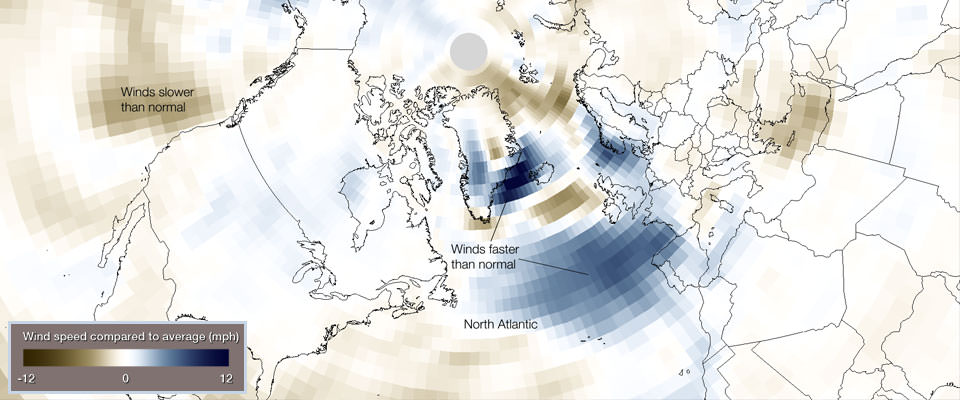
Fourteen of 20 hurricane-force wind events underwent bombogenesis in the North Atlantic during the first two months of 2014. This unusual activity can be seen in wind speed data from the period. In this image, blues indicate areas with wind speeds that are faster than the 30-year historical average (1981-2010).
Bombogenesis, a term used by meteorologists, occurs when a midlatitude (the latitudes between the tropics and polar regions) cyclone rapidly intensifies, or strengthens, over a 24 hour period. This intensification is represented by a drop in millibars, a measurement of pressure used in meteorology. The intensification required to classify as "bombogenesis" varies by latitude. At 60 degrees latitude, it is a drop of at least 24 millibars (24 hectopascals) over 24 hours. At the latitude of New York City, the required pressure drop is about 17.8 millibars (17.8 hectopascals) over 24 hours.
Bombogenesis can happen when a cold air mass collides with a warm air mass, such as air over warm ocean waters. It is popularly referred to as a bomb cyclone.
Social